The ongoing U.S. trade war, marked by steep tariffs on imports, is threatening the anime industry’s critical North American market. With new economic barriers in place, Japanese companies face challenges in maintaining their foothold in one of their most lucrative regions for anime content and merchandise.
Impact of Tariffs on Anime Merchandise
The U.S. recently imposed tariffs as high as 54% on many anime-related imports, particularly merchandise manufactured in China for Japanese companies. This includes items like anime figures, which are now taxed under the “country of origin” rule, even if shipped from Japan.
Additionally, the removal of the $800 de minimis exemption means that even small purchases will incur significant fees, making it costlier for American anime fans to buy directly from Japan or China.
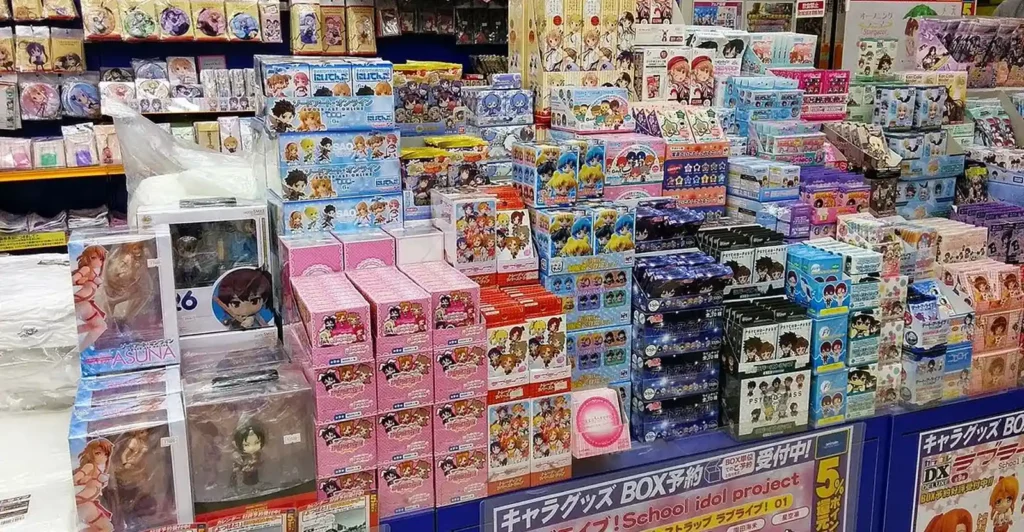

This sharp increase in import costs is expected to reduce demand in the U.S., where merchandise sales have traditionally formed a major revenue stream for Japanese anime companies. For example, services like Buyee, which facilitate cross-border purchases of anime goods, are already preparing to comply with the new tariff rules while exploring ways to ease customs payments for consumers.
Shifting Focus to Emerging Markets
As North America becomes a less viable market due to these trade barriers, Japanese anime companies are increasingly eyeing emerging markets like Latin America and Southeast Asia. These regions saw significant growth in cross-border e-commerce purchases of anime merchandise in 2024—up 58% and 44%, respectively. This diversification could help offset losses from the U.S., but it may take time to replicate the scale and profitability of the North American market.
China also presents opportunities as its interest in Japanese films and anime has surged. In 2024, Chinese cinemas screened a record number of Japanese films, with anime dominating box office earnings. However, geopolitical tensions and China’s growing domestic animation industry could limit long-term reliance on this market.
Streaming: A Resilient Revenue Stream
While merchandise sales face headwinds, streaming revenue remains relatively insulated from tariffs. The U.S. is a major contributor to global anime streaming revenue, accounting for nearly half despite comprising only 7% of the world’s population. Streaming platforms like Netflix and Crunchyroll have strong operating margins and are likely to absorb potential currency fluctuations caused by the trade war without passing costs onto consumers.
This resilience is critical as streaming has become a cornerstone for distributing anime globally. Unlike physical goods, digital licensing is not subject to import tariffs, allowing companies to continue leveraging platforms to reach U.S. audiences.
Challenges for Smaller Studios
The trade war’s ripple effects extend beyond merchandise and streaming. Smaller Japanese studios already face financial struggles due to shrinking budgets for traditional TV and film contracts. In 2024 alone, six anime studios declared bankruptcy as competition intensified amid a shift toward digital media production. These challenges could be exacerbated if U.S.-based distributors reduce investments due to higher costs.
The U.S.-Japan trade war poses significant risks to the anime industry’s key North American market. While streaming offers some protection against tariffs, merchandise sales, a cornerstone of revenue are likely to decline due to increased costs for American consumers.
To mitigate these challenges, Japanese companies are exploring growth opportunities in emerging markets like Latin America and Southeast Asia while continuing to capitalize on streaming’s global reach.
However, the long-term impact will depend on how trade negotiations evolve and whether Japan can secure exemptions or reduced tariffs for its exports.
For now, both businesses and fans must brace for a more expensive and uncertain future in the world of anime commerce.